MIDTERM NOTES
Created Wednesday 25 May 2016
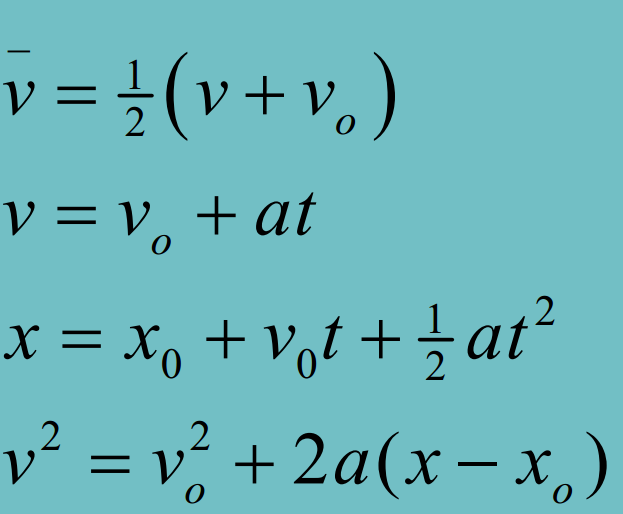
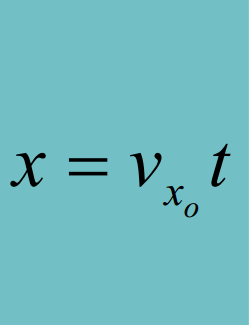
Dimension: Classification/Nature of physical quantity
Unit: Standard of measurement of a physical quantity
Dimensions
distance -> L
time -> T
mass -> M
Dimensional homogeneity means only quantities with the same dimensions may be compared, equated, added, or subtracted.
Basically only stuff with same dimensions can be used mathematically.
| Quantity | SI Unit | Other SI Unit | Dimension |
|---|---|---|---|
| Force | kgms^-2 | N | MLT^-2 |
| Energy | kgm^2s^-2 | J | ML^2T^-2 |
| Power | kgm^2s^-3 | W | ML^2T^-3 |
| Momentum | kgms^-1 | MLT^-1 | |
| Impulse | kgms^-1 | MLT^-1 |
----------
MIDTERM PREP STARTS HERE
----------
PDF 1
Distance != Displacement
Average Speed != Average velocity
Speed -> Distance
Velocity -> Displacement
Average acceleration -> Change in velocity
Negative acceleration != Deceleration
"Negative acceleration is acceleration in the negative direction
as defined by the coordinate system."
"Deceleration occurs when the acceleration is opposite in
direction to the velocity (i.e. slowing down)"
Integration gets you the area under the curve
for relative velocity
V(BW) is the velocity of the boat in the water frame - it is equal to V(B)-V(W)